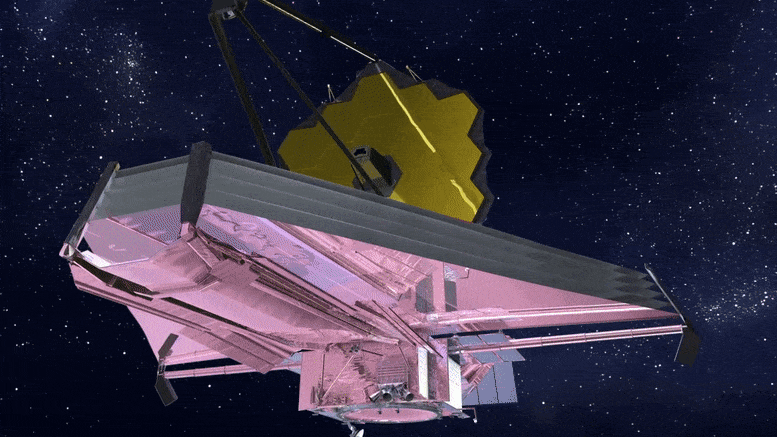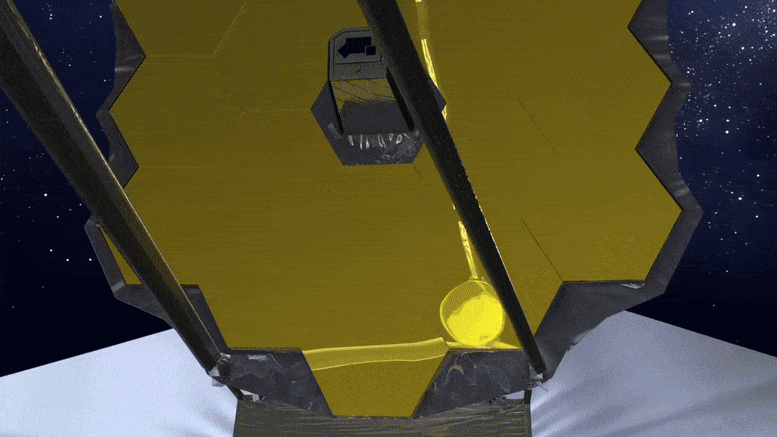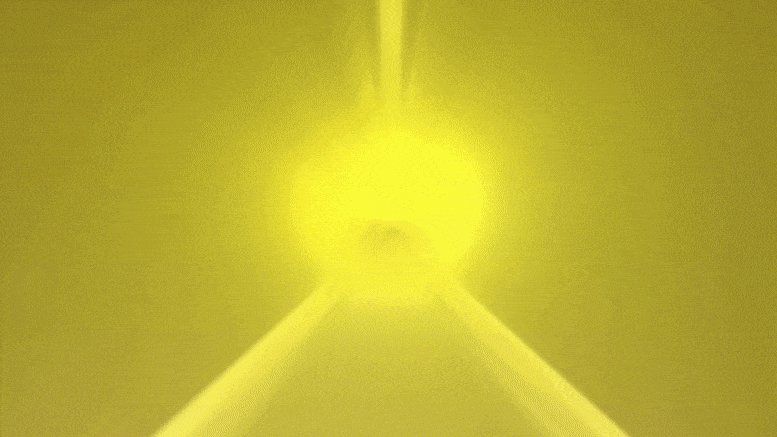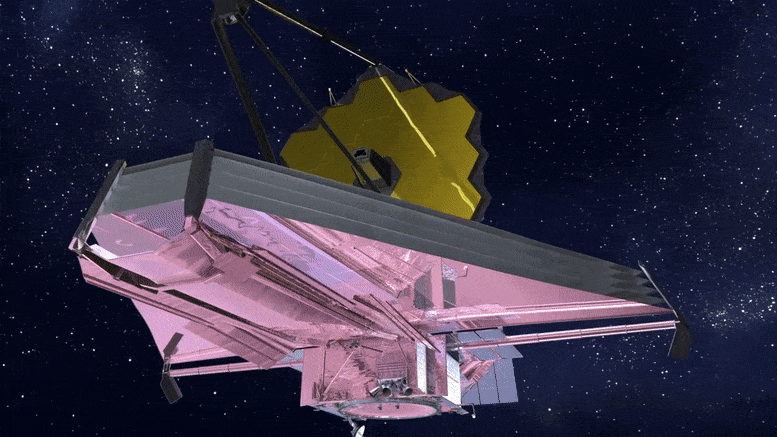
Le télescope spatial James Webb de la NASA. Crédit : NASA Goddard Space Flight Center et Northrup Grumman
Commence maintenant le processus d’alignement des 18 segments de miroir afin qu’ils fonctionnent ensemble comme un seul.
Depuis l’arrivée de[{ » attribute= » »>NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope at its orbital destination January 24, the mission operations team has successfully powered on all of the telescope’s science instruments, including its primary camera, the Near Infrared Camera, or NIRCam, built by a team of researchers and engineers led by University of Arizona astronomer Marcia Rieke.
Turning the instruments on is the first in a series of critical steps that also includes turning off heaters to begin a long cool-down process for the instruments and aligning the telescope’s mirrors over a period of months.
Launched on December 25, Webb is NASA’s top science priority, and UArizona astronomers played key roles in designing and developing the telescope’s infrared eyes. NIRCam and MIRI, which stands for Mid-Infrared Instrument, will allow Webb to peer deeper into the cosmos than ever before and collect light from the earliest stars, galaxies, nebulous stellar nurseries, planetary atmospheres, and more.
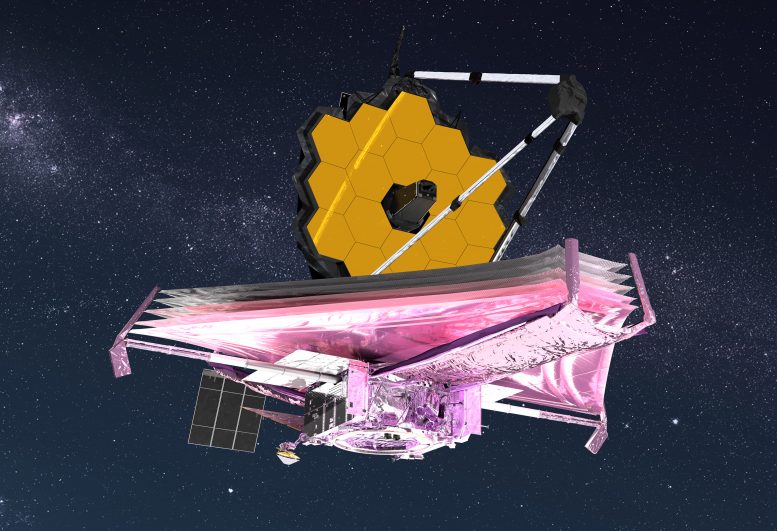

The James Webb Space Telescope has reached it’s parking spot in space and has successfully powered up all of it’s instruments. Within the week, the UArizona-led NIRCam will be used to align the 18 gold-plated mirror segments to work together as one giant mirror.. Credit: NASA GSFC/CIL/Adriana Manrique Gutierrez
Marcia Rieke, a University of Arizona Regents Professor of Astronomy, is principal investigator for NIRCam. Her husband, George Rieke, also a Regents Professor of Astronomy, is the science team lead for MIRI.
While MIRI and some components of the telescope’s other instruments were powered on in the weeks after Webb’s December 25 launch, the final three instruments – including NIRCam – turned on in the past few days.
After the powered-on instruments undergo initial checks, the mission operations team’s next major step is to turn off instrument heaters. The heaters keep critical optics warm to protect them from water and ice condensation. As the instruments meet predefined criteria for overall temperatures, the team will shut off the heaters to allow the instruments to cool to final temperatures that will allow the infrared detectors to see faint objects in the night sky.
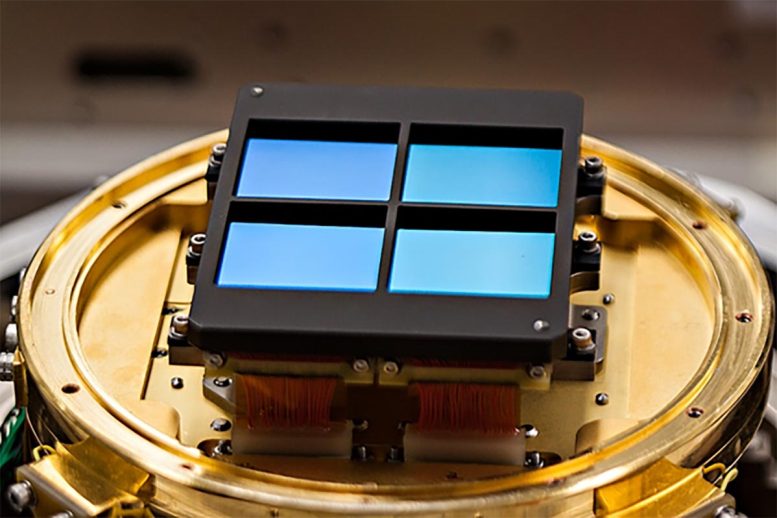
A sensor array for the NIRCam instrument, designed and tested by Marcia Rieke’s research group at Steward Observatory. For the sensors to detect infrared light without too much noise in the data, Webb and its instruments must be kept as cool as possible. Credit: Marcia Rieke
When NIRCam reaches about minus 244 degrees Fahrenheit, likely later this week, Webb’s optics team will be ready to begin meticulously aligning the telescope’s 18 primary mirror segments to work together as a single mirror surface. NASA is targeting star HD84406 to begin this process. It will be the first object NIRCam sees when photons of light hit the instrument’s powered-on detectors. However, it won’t be the first image that is shared with the public. That object has not been chosen yet, and NASA will likely release the image this summer.
NIRCam was assigned the task of aligning the telescope because it was built to observe shorter wavelengths of light than the other onboard instruments. Because of this, it can discern the most detail and is the most sensitive to misalignment.
“These first photos mean that we finally get starlight moving through the system and detected by NIRCam,” Marcia Rieke said. “NIRCam has not been turned on since before launch; this will prove the launch didn’t introduce issues for how it can work.”
Étant donné que les 18 segments de miroir ne fonctionnent pas encore en tandem, le processus d’alignement créera d’abord une image de 18 points de lumière aléatoires et flous lorsque le télescope pointe vers l’étoile HD84406.
Pendant les premières semaines d’alignement des miroirs, l’équipe gardera NIRCam formé sur l’étoile tout en effectuant des ajustements microscopiques sur les segments de miroir de Webb. En fin de compte, cette collection de 18 points flous deviendra une image focalisée d’une seule étoile.
Le refroidissement du télescope et des instruments se poursuivra au cours du mois prochain, NIRCam atteignant finalement près de moins 400 degrés Fahrenheit.
La NASA a alloué 13% du temps d’observation total de Webb aux astronomes de l’UArizona. Cela donne à l’université plus de temps de visionnage que tout autre centre d’astronomie dans le monde. La National Science Foundation a classé l’Université de l’Arizona No. 1 en astrophysique et dépenses de recherche en astrophysique chaque année depuis 1988.

« Évangéliste généraliste de la bière. Pionnier du café depuis toujours. Défenseur certifié de Twitter. Internetaholic. Praticien du voyage. »





More Stories
Rencontrez du saumon aux dents hautement minéralisées
Mission Starlink mardi depuis Cap Canaveral
La préparatrice physique révèle les trois aliments qu'elle mange chaque jour